Mri Body Fat Measurement
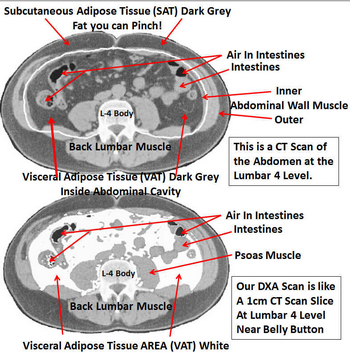
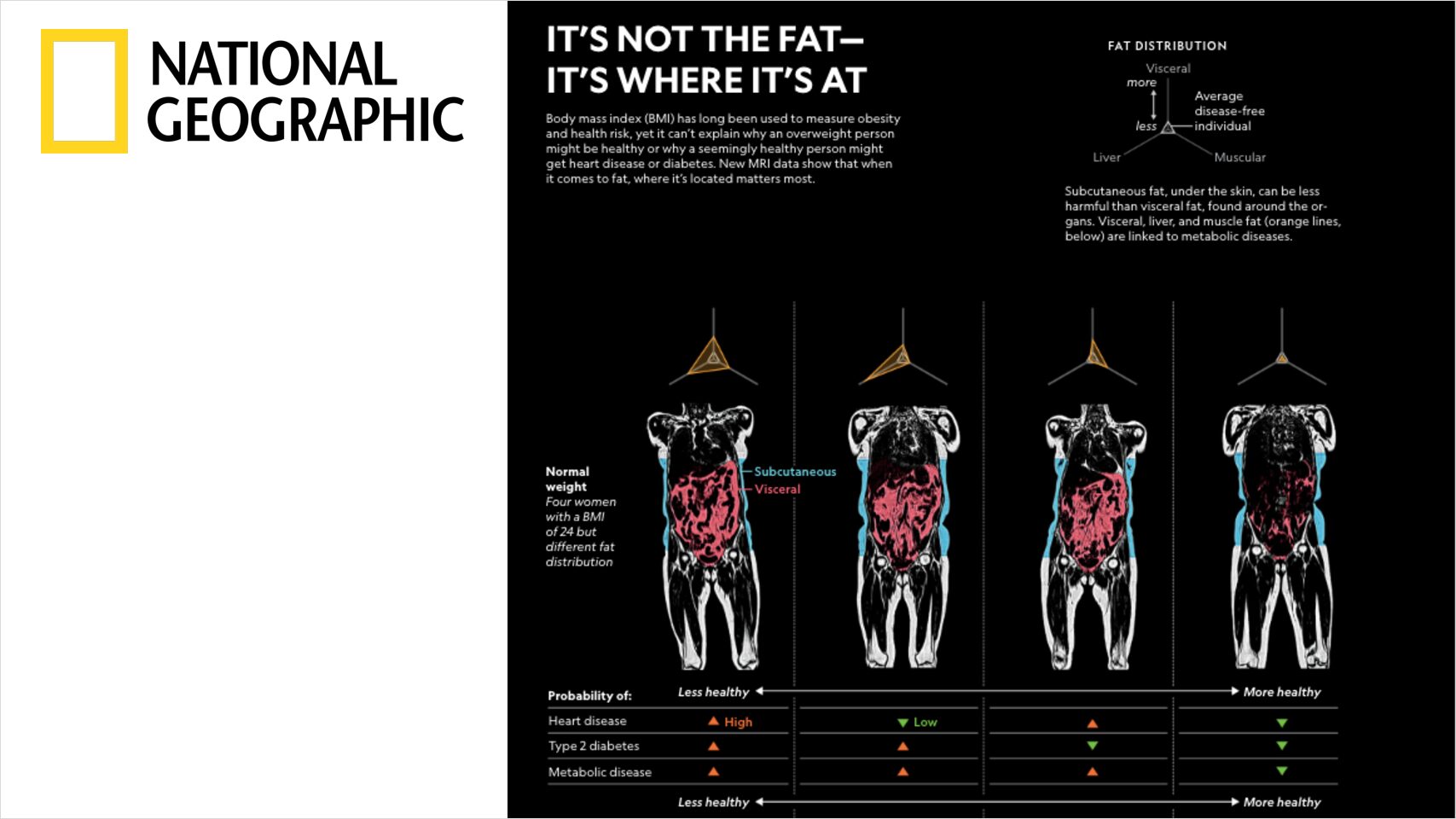
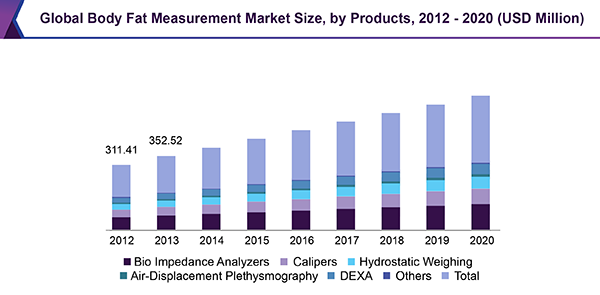
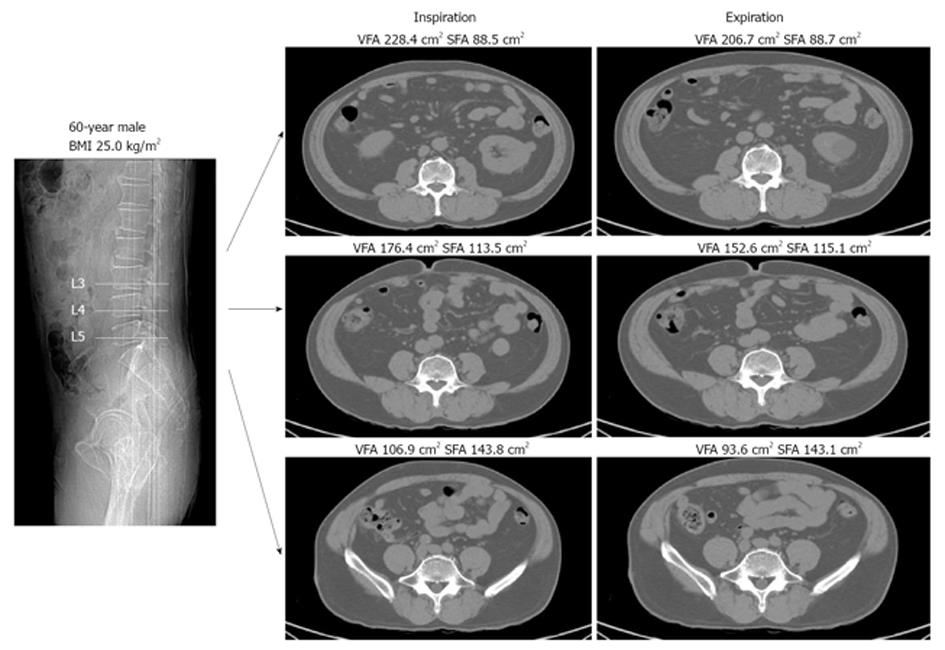
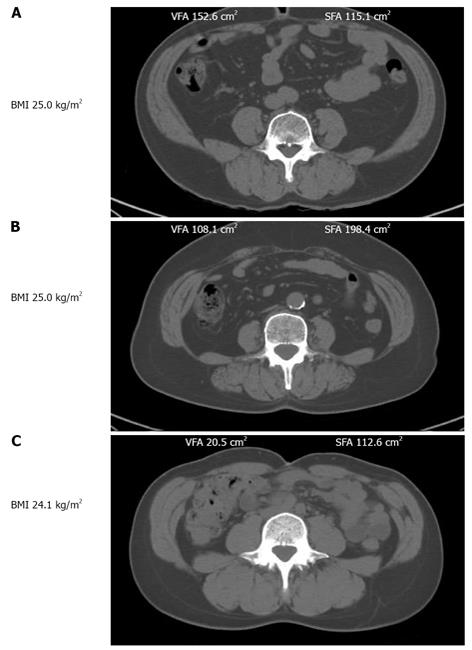
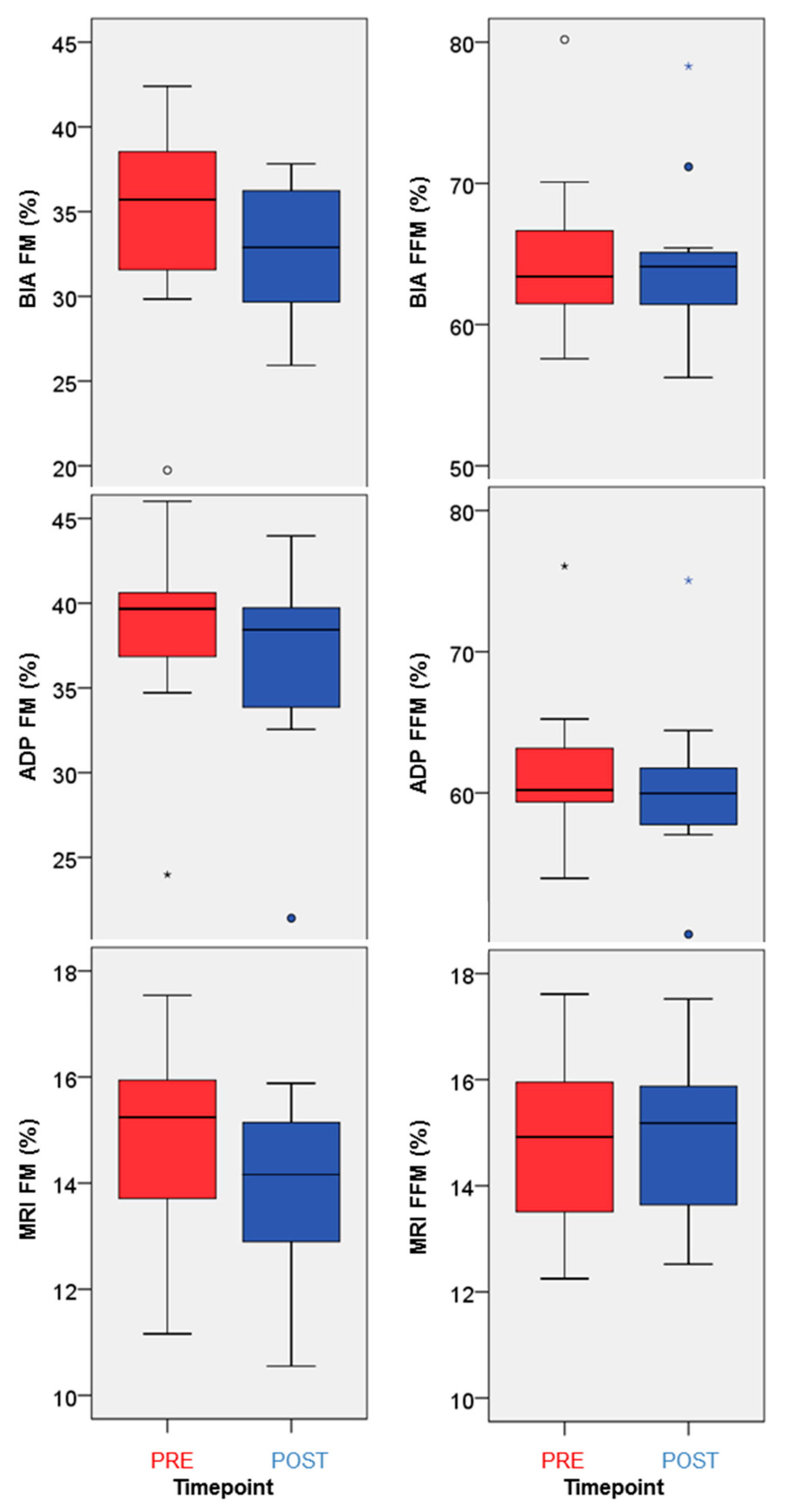
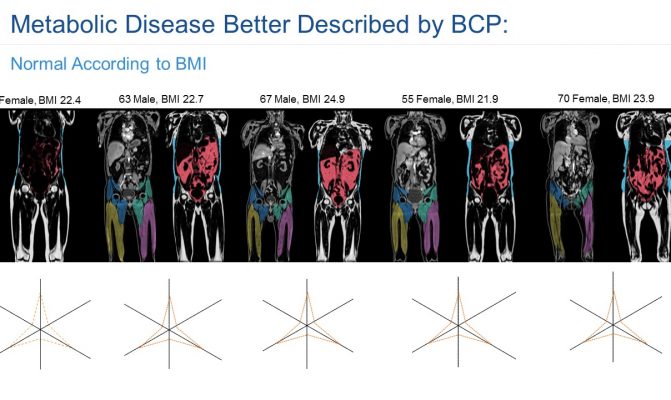
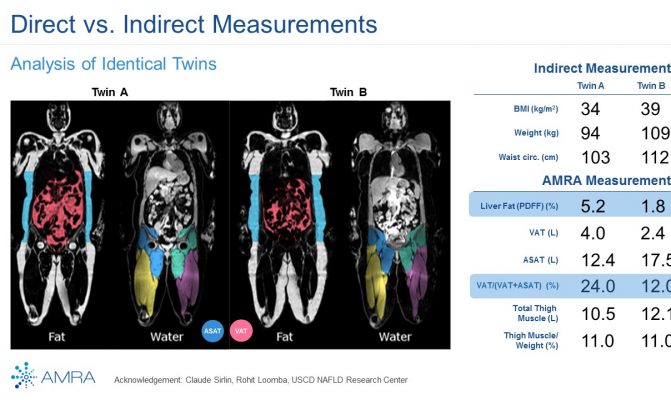
In this study we assessed different magnetic resonance imaging mri scanning regimes and examined some of the assumptions commonly made for measuring body fat content by mri. Tbf nfatvoxels voxeldim fatdensity where nfatvoxels is the total number of fat voxels contained in the data set voxeldim is the voxel dimension in cm 3 and fatdensity is the density of the fat tissue in gcm 3. The total at measured by mri was converted to total fat mass again assuming that most of the fat resided in at and using a constant density of 094 kgl. 29 figure 5 shows an example of hepatic imaging in a subject with hepatic steatosis and severe dyslipidemia before and after treatment of the dyslipidemia with plasmapheresis and multidrug therapy. Mri can decompose the liver signal into fat and water components and measure liver fat more directly than ultrasound or ct. The whole body mri results showed that there was a significant variation in the percentage of total internal as well as visceral adipose tissue across a range of adiposity which could not be predicted from total body fat andor.
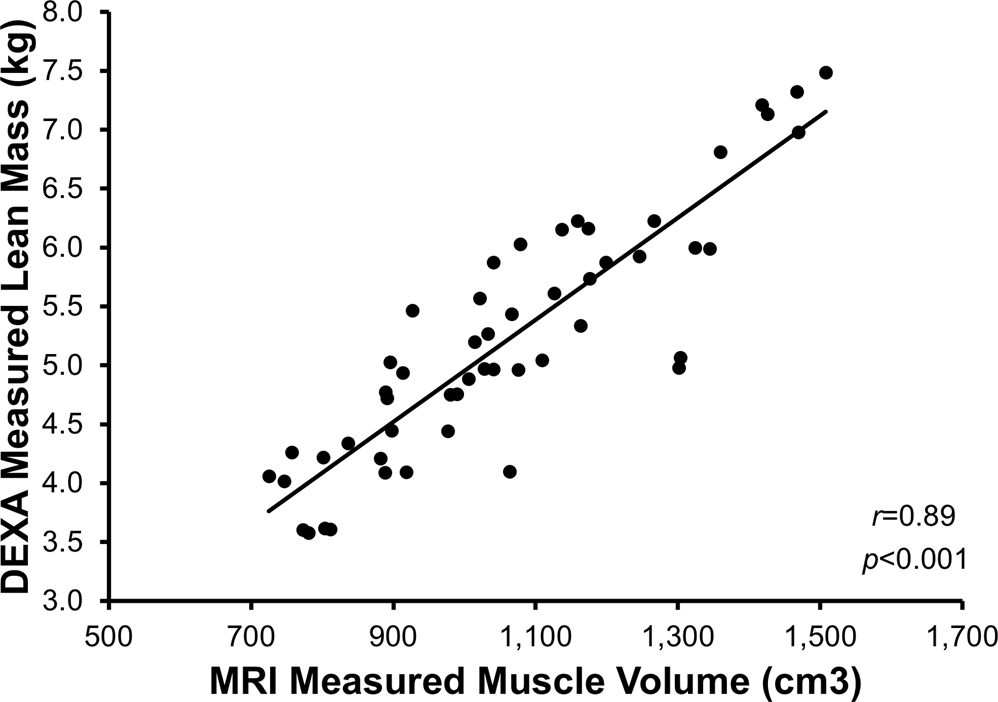
These scans can provide the most precise body composition measurements especially for intra abdominal fat measurement. Mri that is used to diagnose and treat medical conditions. They are expensive however and are usually not indicated solely for measuring body fat. Body fat can also be estimated using cross sectional imaging methods such as magnetic resonance imaging mri nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and computerized tomography ct. The linear correlation between body fat mass measured by bia and at volume measured by mri was 075 and 081 for females and males respectively. Whole body mri was used to quantify and study different body fat depots in 67 women.
In terms of body composition the high quality images can be processed to differentiate and measure the amounts of fat and lean body tissue and their distribution. Calculation of the total body fat tbf is performed using the following formula.
Random Post
- body composition and anthropometric measurement
- usaf body fat measurement
- kohls bra measurement
- whole body protein synthesis measurement
- yasmeen ghauri body measurement
- take body measurements without measuring tape
- olay body measurement
- body measurements according to height
- quad body measurement
- kim go eun body measurement
- dry body measurement
- debenhams bra measurement
- krunal pandya body measurement
- body measurement tracking chart pdf
- body mass index measurement in schools
- ananya pandey body measurement
- normal man body measurements
- red velvet wendy body measurements
- measurement for bra cup sizes
- jessica lucas body measurement
- amy carlson body measurement
- arpita khan body measurement
- shivangi joshi body measurement
- marina sirtis body measurement
- can you add body measurements to fitbit
- irene red velvet body measurement
- what is a good measurement for a woman's body
- body measurement mhw
- body measurement meaning in hindi
- ava max body measurement
- bra measurement size guide
- weight and body measurement chart
- armeena khan body measurement
- arianny celeste body measurement
- virginia gardner body measurement
- the perfect woman's body measurement
- athletic body measurements
- how to figure out body measurements
- measurement of the force of blood moving around the body
- tamil actress body measurements
- male vs female body measurements
- blogilates body measurement
- body measurement chart for tailoring
- gabrielle union body measurement
- jeff cavaliere body measurement
- shaista lodhi body measurement
- rishabh pant body measurement
- anup thakur body measurement
- conor mcgregor body measurement
- ketone body measurement kit